Food safety failures are rare. In the majority of cases, dangerous bacteria are cultivated due to the presence of the appropriate conditions. FATTOM is the food safety model that describes precisely what those conditions are and how food companies can manage them.
In simple terms, FATTOM identifies the six factors that enable bacteria to proliferate in food. Food operators’ awareness and control of these forces will significantly reduce the likelihood of foodborne illness, regulatory infractions, and business interruption.
In this guide, we will discuss the meaning of FATTOM, the importance of this concept in contemporary food operations, and how regulatory compliance management software such as Jadian can assist food businesses in managing these risks on a large scale.
What Is FATTOM in Food Safety?
FATTOM is an environmental acronym of the six conditions of the environment required by bacteria to grow. When any of these factors exist and are not under control, dangerous microorganisms would multiply quickly.
The FATTom food safety model is commonly applied in:
- HACCP softwares
- Food handler training
- Regulatory inspections
- Risk assessment of restaurants and food manufacturing.
Knowledge of FATTOM assists food enterprises in controlling their food hygiene.
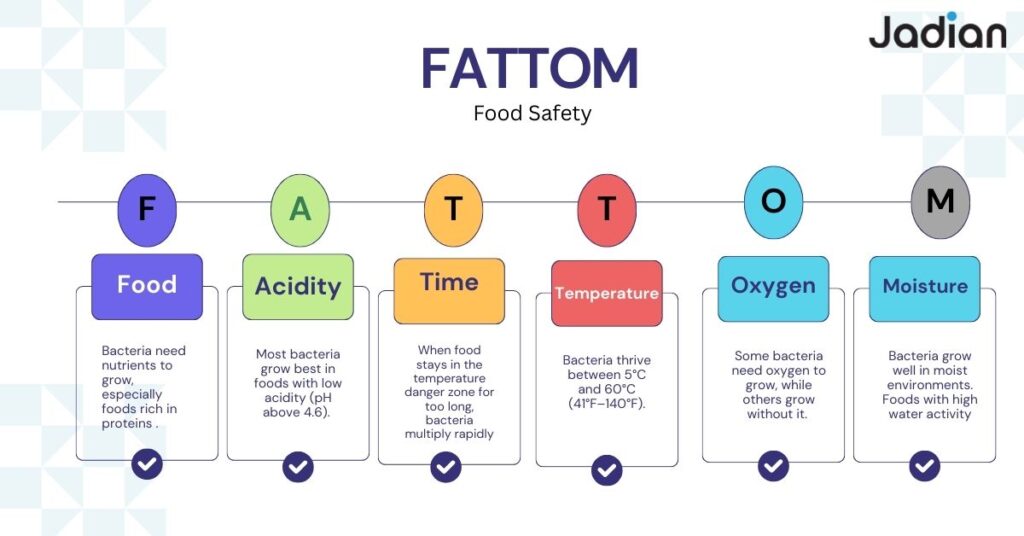
The six FATTOM factors are:
- F – Food
- A – Acidity
- T – Time
- T – Temperature
- O – Oxygen
- M – Moisture
All the factors are controllable points of risk. When food operators are in control of all six, food safety is predictable and not unpredictable.

What Does FATTOM Stand For?
The acronym FATTOM is used to refer to the Food, Acidity, Time, Temperature, Oxygen, and Moisture. All these factors characterize the most favorable bacterial environment.
The key takeaway is simple:
In case the food has nutrients, is of the right acidity, remains too long under unsafe temperatures, and has oxygen and moisture, it will allow bacteria to grow.
We will consider each separately and discuss how those elements can be managed by food businesses.
F in FATTOM (Food): What Does This Mean?
Food is defined as nutrients required to enable bacteria to survive and reproduce. The majority of the bacteria that cause diseases flourish in protein and carbohydrate-rich foods.
Foods are not equally risky from the perspective of food safety. There are naturally low-risk foods and foods that will make the best media for bacterial growth.
Some of the high-risk foods are:
- Meat and poultry
- Seafood and shellfish
- Dairy products
- Cooked rice and pasta
- Eggs
- Cooked vegetables
- Gravies and sauces
These are called TCS foods ( Time/Temperature Control for Safety foods).
The Importance of Food Type in Food Safety
To grow, bacteria are in need of nutrients. Protein-dense and moist foods supply:
- Amino acids
- Sugars
- Minerals
When bacteria are exposed to these nutrients, they grow very fast, provided the conditions are favorable.
The Role of Compliance Software in Dealing with Food Risks
Food businesses are assisted through regulating compliance management software such as Jadian:
- Categorize high-risk food.
- Automated HACCP controls.
- Monitor ingredient risk profiles.
- Automatize food safety practices.
Jadian minimizes the use of memory and manual logging in order to digitize food safety documentation.
What is the Meaning of the “A” in FATTOM? (Acidity)
The A in FATTOM is Acidity and the pH of a food. The pH level has a direct relation to bacterial survival and multiplication.
Core takeaway:
The majority of the pathogenic bacteria multiply in food pH of 4.6-7.5, which is neutral or slightly acidic.
PH and Food Safety
High acid levels (low PH) inhibit or retards bacterial growth.
Low acid (high PH) promotes the growth of bacteria.
Examples:
| Food | Approximate pH | Risk Level |
| Lemon juice | 2.0 | Low risk |
| Vinegar | 2.5 | Low risk |
| Tomatoes | 4.2–4.9 | Moderate |
| Milk | 6.5 | High |
| Cooked meat | 5.5–6.5 | High |
Why Acidity Control Matters
Lack of proper control of acidity can:
- Neutralize preservatives
- Invalidate safe recipes
- Create regulatory violations.
This is particularly imperative in:
- Fermentation
- Pickling
- Sauce production
- Beverage manufacturing
How Jadian aids in the control of acidity
Jadian compliance management software assists companies in:
- Track recipe formulations
- Document pH testing records
- Implement checking schedules.
- Produce audit-ready compliance reports.
This will guarantee that acidity controls are uniform, proven, and inspection-compliant.
What Is the First “T” in FATTOM? (Time)
Time is the amount of time food remains in a condition that will allow the bacteria to grow. Even safe food will turn into risky food when it is kept too long within the threat zone.
Core takeaway:
The higher the temperatures are kept on food, the higher the risks of bacterial growth.
The danger zone concept
The normal food safety danger zone is normally:
5degC to 60degC (41degF to 140degF)
Within this range:
- Bacteria have the ability to replicate in 20 minutes.
- Food spoils quickly than anticipated.
Common time-related risks
- Slow cooling of cooked food
- Improper hot holding
- Extended prep times
- Lost food on service.
Time control best practices
- Reduce time at the danger zone.
- Adhere to rigid timetables in cooling.
- Use clear discard rules
The way Jadian assists in Time Risk Management
Food businesses can use Jadian to:
- Automate time-based alerts
- Digitize cooling logs
- Track preparation and holding time.
- Assure accountability of staff.
This eliminates conjecture and enhances intershift consistency.
What Is the Second T in FATTOM? (Temperature)
The most important control point of food safety is temperature. Mistemperatures are among the major causes of food poisoning.
Core takeaway:
Temperature control will ensure that there is no growth, survival, or propagation of bacteria.
Safe temperature standards:
Cold holding: ≤ 5 °C (41 °F)
Hot holding: ≥ 60 °C (140 °F)
The temperatures of cooking differ depending on the food.
Examples of temperature abuse occur when:
- Refrigeration fails
- Hot food cools too slowly
- Food is reheated improperly
The Importance of Temperature Monitoring
The temperature variations are usually ignored until they manifest as:
- Illness occurs
- An inspection fails
- The product must be discarded
How Jadian Enhances Temperature Compliance
The Jadian compliance software permits:
- Online temperature recording
- Deviation alerts, which are automated
- Globalized surveillance of sites
- Audit-ready records
This guarantees a constant state of conformity without the use of paperwork.
What Does the “O” in FATTOM Mean? (Oxygen)
Oxygen defines the growth of aerobic or anaerobic bacteria. There are bacteria that cannot survive without oxygen, and others can.
Core takeaway:
Oxygen control is important as different bacteria can grow in various conditions of oxygen.
Food Safety Hazards Associated with Oxygen
- Improper vacuum sealing
- Modification to the atmosphere pack failure.
- Improper storage procedures
Examples:
- Clostridium botulinum is an anaerobic gram-positive bacterium
- Salmonella proliferates in the presence of oxygen
Oxygen Control Strategies
- Proper choice of packaging.
- Strict storage procedures
- Labeling instructions and handling instructions.
How Jadian Enhances Oxygen Compliance
Jadian helps document:
- Packaging methods
- Storage requirements
- Process validation records
This enhances traceability and regulatory assurance.
What is the M of the FATTOM? (Moisture)
The moisture is “water activity” that is important in the growth of bacteria. The greater the water availability in food, the more the risk.
Core takeaway:
Bacteria require the presence of water to flourish, and managing water activity will diminish the chance of food being contaminated.
High-moisture foods include:
- Fresh meat
- Cooked grains
- Dairy products
- Sauces
Moisture control methods
- Drying
- Salting
- Sugaring
- Dehydration
The Importance of Moisture Monitoring
The presence of high moisture, warmth, and nutrients gives perfect conditions for growth.
How Jadian helps with Moisture-Related Compliance
Jadian allows businesses to:
- Track process controls
- Use standardized procedures.
- Document hazard controls
This will make sure that moisture risks are always under control.
What Is the Importance of FATTOM in the Food Industry?
FATTOM is a very important tool, since it describes the cause of foodborne illness. It offers a scientific foundation of food safety controls.
Application of FATTOM in the food industry
- Supports HACCP plans
- Improves staff training
- Improves inspection preparedness
- Reduces food waste
- Protects brand reputation
Regulatory Expectations
Food authorities require businesses to:
- Understand microbial risks
- Apply preventive controls
- Keep recordable documents.
The Role of Compliance Software in Strengthening FATTOM Implementation
Manual systems do not work because of:
- Human error
- Inconsistent documentation
- Missing records
Jadian compliance management software assists food establishments:
- Concentrate on compliance documents.
- Uniformize FATTOM-based controls.
- Monitor and report automatically.
- Streamline audits and inspections.
This transforms food safety to be a burden to a business advantage.
What Are The Active Ways In Which Food Businesses Can Manage FATTOM Risks in their Daily Operations?
FATTOM can be most effectively handled through regular, documented daily practice rather than a single training session. Risks in food safety do not arise during special events, but in the normal running of operations.
It is important to understand the FATTOM conceptually, but it is its operational application that safeguards the customers, employees, and the business in general. This section is devoted to the manner in which food businesses could proactively operate each factor of FATTOM in real-life settings like restaurants, cafes, cloud kitchens, and food manufacturing facilities.
Why does FATTOM Control not qualify as a single-time undertaking?
The risks at the FATTOM vary during the day as the food passes through the stages of preparation, storage, cooking, holding, and service. What is safe at 9 a.m. might be unsafe at noon due to the failure of controls.
Variability is brought about by daily operations because of:
- Staff changes
- Equipment performance
- Service rushes
- Environmental conditions
Due to this variability, there is no use of static food safety plans. Monitoring has to be done actively.
What Are the Daily Controls on How food (F) Risks?
Proper food classification and handling are a starting point of food risk control every day. The personnel should be aware of the high-risk ingredients and those that need stricter measures.
Effective day-to-day controls entail:
- Clear labeling of TCS foods
- First in, first out (FIFO) systems
- Raw and the ready-to-eat foods
- Vetting of approved suppliers
These practices cannot be easily checked in the process of inspection without documentation.
How Jadian helps:
Jadian allows businesses to:
- Keep electronic records of ingredients
- Give food items risk categories
- Track supplier approvals
- Standardize processes of handling
This allows the risks associated with food to be continuously controlled in shifts and areas.
How does one control Acidity (A) in an Operational Environment?
The risks of acidity tend to occur when changing recipes or substituting them, and when they are not prepared correctly. Deviations as little as these may interfere with pH and endanger food safety.
Typical acidity-related operating risks are:
- Variations in the duration of fermentation
- Misplaced ratios of the ingredients
- The absence of steps of pH verification
- Employees who are dependent on visual aids rather than testing
Acidity management on a daily basis requires:
- Defined pH targets
- Testing schedules
- Clear corrective actions
How Jadian helps:
Jadian allows food companies to:
- Digitally store approved recipes
- Record pH test results
- Alerts on limits beyond which the values fall
- Keep records of the inspection of inspectors
This makes acidity control an auditable and quantifiable process.
What Is the Time (T) Control to Use in the Busy Periods of Service?
Time system malfunctions are mostly caused during peak periods. In case the staff is in a hurry, the food can spend excessive time at unsuitable temperatures.
High-risk scenarios include:
- Ready-prepared food left on service
- Slow cooling of food after cooking
- Long waiting in the buffets or the catering
Nevertheless, good time controls are based on:
- Clear time limits
- Visual or digital reminders
- Defined discard rules
How Jadian helps:
With Jadian, businesses can:
- Prep and holding times are digitally recorded
- Get automatic reminders.
- Unify discard policies.
- Loosen dependence on staff memory
This guarantees that time constraints are taken care of even when stress is high.
What Can Be the Consistent Temperature (T) Control?
The most monitored FATTOM factor is temperature control, butit is the most violated factor. Manual temperature records are usually incomplete, inaccurate, or not taken at all.
Examples of daily life temperature problems are:
- Overloaded refrigerators
- Faulty equipment
- Infrequent checks
- Inconsistent logging
To control temperature, businesses require:
- Established monitoring rates.
- Clear corrective actions
- Verified records
How Jadian helps:
The temperature control in Jadian is centralized by:
- Automating temperature records
- Real-time deviation flagging
- Developing automatic trail audits
- Sustaining multi-location management
This minimizes areas of compliance and speeds up response.
What Is the Impact of Oxygen (O) Control on Food Safety in Everyday Life?
Oxygen control is an aspect that is not given much attention since it is not as noticeable as temperature or time. Nevertheless, improper oxygenation may cause severe dangers.
The operational risks include:
- Improper vacuum sealing
- Poor labelling of low-oxygen food
- Improper packaging of foods
Oxygen needs to be managed daily and includes:
- Staff awareness
- Appropriate packaging processes
- Clear storage instructions
How Jadian helps:
Jadian favours controls concerning oxygen through:
- Recording the packaging technique
- Streamlining storage processes
- Documentation of validation examinations
This enhances traceability and minimizes the threat of hazardous anaerobic development.
What can be done to Control Moisture (M) in Food Preparation Areas?
The moisture control is very important since the water activity directly impacts the survival of bacteria. When it is warm and humid, it is dangerous because of the moisture.
Risks associated with moisture on a daily basis are:
- Unprofessional drying of machines
- Cold storage condensation
- Unstable drying/curing processes
To be effectively moistened, it is necessary:
- Sanitary habits
- Equipment maintenance
- Documented procedures
How Jadian helps:
Jadian allows businesses to:
- Sanitization of documents
- Track equipment cleaning
- Enhance moisture control SOPs
This also makes sure that risks of moisture are prevented in advance as opposed to finding them during inspections.
What are the advantages of Digital Compliance over FATTOM Control in the Paper Systems?
The use of paper-based food safety systems is unsuccessful in that it is based on memory, honesty, and availability. These weaknesses are minimized by digital compliance systems.
The main benefits of digital compliance management are:
- Real-time visibility
- Standardized processes
- Reduced human error
- Faster corrective actions
- Easier audits
Paper logs often:
- Go missing
- And are filled in with hindsight.
- Contains inconsistent data
IT systems establish accountability and transparency.
Why Does Jadian Work Well with Food Safety Management with FATTOM?
Jadian will also be set out to deal with regulatory compliance, as a whole, rather than checklists. This renders it particularly useful for the risk control of FATTOM.
Food business strengths of Jadian:
- Customizable workflows
- Centralized documentation
- Automated warning and reporting
- Scalable across locations
- Audit-ready at all times
Businesses that employ Jadian are always in compliance, as opposed to responding to inspections.
How Can You Train Employees in a Way FATTOM KM Sticks (Even When Turnover)?
The failure of food safety training is possible because it is perceived as a one-time initiation process. Food service high turnover requires that training be structured as a system: repeatable, role-based, and measurable.
Rather than everybody learning everything, role-based design training:
- Prep staff: prep module-based training
- Service staff: modules oriented towards processing and retaining rules
- Supervisors: targeted modules regarding surveillance and remedial measures
- Verification and audit readiness: dedicated modules for managers
Working training uses competence checks.
Instead of inquiring about training attendance. is asking:
- Can you demonstrate it?
- Do you know a risk situation?
- Are you able to make the right selection?
Simple competence methods:
- Speedy scenario quizzes (5 minutes)
- Hands-on checks during shift
- Registered supervisor sign-outs were linked to actual work.
How Jadian helps:
Jadian can facilitate training compliance by:
- Role-based training assignments
- Monitoring completions and refreshment of cycles
- Checking logging competency and supervisor validation
- Creating evidence in the course of audits that training is not a thing of the past
This transforms education into more of a paper compliance rather than actual working reliability.
What is the Relationship between Supplier and Ingredient Control and the FATTOM-Based Risk Management?
Food safety is not just about being managed within your facility. A significant amount of risk comes in via:
- Ingredients
- Packaging
- Delivery conditions
- The way suppliers are managed
Internal controls can be perfect, and the supplier control can be weak.
How supplier controls appear in a real system.
- Criteria of supplier approval (licenses, audits, certifications)
- Ingredient specification (storage, shelf life, allergen information)
- Checks on delivery acceptance (condition, labeling, documentation)
- Traceability preparedness (lot/batch tracking, ability to recall)
Why do regulators care about this?
What is the interest of regulators in this?
When conducting investigations, the regulators usually enquire:
- Where did it come from?
- Can you trace it?
- And who did you know who got it?
- Is it possible to isolate infected batches fast?
How Jadian helps:
Supplier compliance can be supported using Jadian compliance management software in the following ways:
- Concentrating on supplier documentation
- Keeping specs and necessary evidence by ingredient
- Delivery acceptance checks are always checked
- Sustaining traceability and recall documentation processes
It is not only concern passing an inspection. It is concerning the opportunity to act confidently in case of an incident.
How to Build an Operational Food Safety Dashboard Managers Really Use?
Managers need not be provided with more data, but with the right signals. An effective compliance perspective puts an emphasis on what is really important:
- What is overdue?
- What has failed?
- What has been repeated?
- What requires verification?
Easy to read dashboard indications (non-repeating logs)
- Stations/site overdue checks.
- Same issue occurring frequently (repeatedly every week)
- Actions to be taken that were taken late
- Training refreshes due
- Maintaining or calibrating equipment
This makes compliance a back-office operation into an operational system of control.
How Jadian helps:
Jadian has the ability to bring these signals into a single view to enable the teams to:
- Spot patterns early
- Prioritize risks fast
- Demonstrate supervision in examinations
And that is a huge benefit compared to the paper files or spreadsheets that are not linked together.
What is the Power of a Good System in Eliminating Wastage and Margins?
The systematic compliance system tends to minimize food waste due to the clarity of decisions made earlier. Once the problems are detected in teams at an earlier stage, the entire batches are not lost.
These operational advantages can be:
- Fewer “just in case” discards
- Quick identification of weak points in the process
- Minimum rework as a result of inconsistencies
- Improved handling with regard to shelf-life
Compliance is not just about punishment. When done properly, it enhances financial performance.
Final Thoughts
The meaning of FATTOM is the key to current food safety. It changes food safety from more of a science into prevention.
With a combination of FATTOM principles and Jadian compliance management software, the food businesses can:
- Reduce risk
- Improve efficiency
- Increase regulatory confidence.
Food safety does not only relate to compliance. It concerns control, consistency, and trust.
Read More >> Best Food Safety Software Guide
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is FATTOM in food safety?
FATTOM is an acronym for Food, Acidity, Time, Temperature, Oxygen, and Moisture.
Why is FATTOM important?
It describes the environment necessary to promote bacterial growth, which will help prevent foodborne disease.
Which foods are the most influenced by FATTOM?
Moist foods rich in protein, meat, dairy, and cooked grains.
What is the relationship between FATTOM and HACCP?
FATTOM is used to find hazards and critical control points.
What is FATTOM stands for?
FATTOM stands for:
F – Food
A – Acidity
T – Time
T – Temperature
O – Oxygen
M – Moisture
These six factors explain the conditions that allow bacteria to grow in food and are a key concept in food safety.
Is it possible to deal with FATTOM risks with the help of software?
Yes. Software such as Jadian is used to monitor, document, and audit in compliance.






